Bootstrap Provider Specification
Overview
A bootstrap provider generates bootstrap data that is used to bootstrap a Kubernetes node.
For example, the Kubeadm bootstrap provider uses a cloud-init file for bootstrapping a node.
Data Types
Bootstrap API resource
A bootstrap provider must define an API type for bootstrap resources. The type:
- Must belong to an API group served by the Kubernetes apiserver
- Must be implemented as a CustomResourceDefinition.
- The CRD name must have the format produced by
sigs.k8s.io/cluster-api/util/contract.CalculateCRDName(Group, Kind).
- The CRD name must have the format produced by
- Must be namespace-scoped
- Must have the standard Kubernetes “type metadata” and “object metadata”
- Should have a
specfield containing fields relevant to the bootstrap provider - Must have a
statusfield with the following:- Required fields:
ready(boolean): indicates the bootstrap data has been generated and is readydataSecretName(string): the name of the secret that stores the generated bootstrap data
- Optional fields:
failureReason(string): indicates there is a fatal problem reconciling the bootstrap data; meant to be suitable for programmatic interpretationfailureMessage(string): indicates there is a fatal problem reconciling the bootstrap data; meant to be a more descriptive value thanfailureReason
- Required fields:
Note: because the dataSecretName is part of status, this value must be deterministically recreatable from the data in the
Cluster, Machine, and/or bootstrap resource. If the name is randomly generated, it is not always possible to move
the resource and its associated secret from one management cluster to another.
BootstrapTemplate Resources
For a given Bootstrap resource, you should also add a corresponding BootstrapTemplate resource:
// PhippyBootstrapConfigTemplateSpec defines the desired state of PhippyBootstrapConfigTemplate.
type PhippyBootstrapConfigTemplateSpec struct {
Template PhippyBootstrapTemplateResource `json:"template"`
}
// +kubebuilder:object:root=true
// +kubebuilder:resource:path=phippybootstrapconfigtemplates,scope=Namespaced,categories=cluster-api,shortName=pbct
// +kubebuilder:storageversion
// PhippyBootstrapConfigTemplate is the Schema for the Phippy Bootstrap API.
type PhippyBootstrapConfigTemplate struct {
metav1.TypeMeta `json:",inline"`
metav1.ObjectMeta `json:"metadata,omitempty"`
Spec PhippyBootstrapConfigTemplateSpec `json:"spec,omitempty"`
}
type PhippyBootstrapConfigTemplateResource struct {
// Standard object's metadata.
// More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#metadata
// +optional
ObjectMeta clusterv1.ObjectMeta `json:"metadata,omitempty"`
Spec PhippyBootstrapConfigSpec `json:"spec"`
}
The CRD name of the template must also have the format produced by sigs.k8s.io/cluster-api/util/contract.CalculateCRDName(Group, Kind).
List Resources
For any resource, also add list resources, e.g.
//+kubebuilder:object:root=true
// PhippyBootstrapConfigList contains a list of Phippy Bootstrap Configurations.
type PhippyBootstrapConfigList struct {
metav1.TypeMeta `json:",inline"`
metav1.ListMeta `json:"metadata,omitempty"`
Items []PhippyBootstrapConfig `json:"items"`
}
//+kubebuilder:object:root=true
// PhippyBootstrapConfigTemplateList contains a list of PhippyBootstrapConfigTemplate.
type PhippyBootstrapConfigTemplateList struct {
metav1.TypeMeta `json:",inline"`
metav1.ListMeta `json:"metadata,omitempty"`
Items []PhippyBootstrapConfigTemplate `json:"items"`
}
Bootstrap Secret
The Secret containing bootstrap data must:
- Use the API resource’s
status.dataSecretNamefor its name - Have the label
cluster.x-k8s.io/cluster-nameset to the name of the cluster - Have a controller owner reference to the API resource
- Have a single key,
value, containing the bootstrap data
Behavior
A bootstrap provider must respond to changes to its bootstrap resources. This process is typically called reconciliation. The provider must watch for new, updated, and deleted resources and respond accordingly.
The following diagram shows the typical logic for a bootstrap provider:
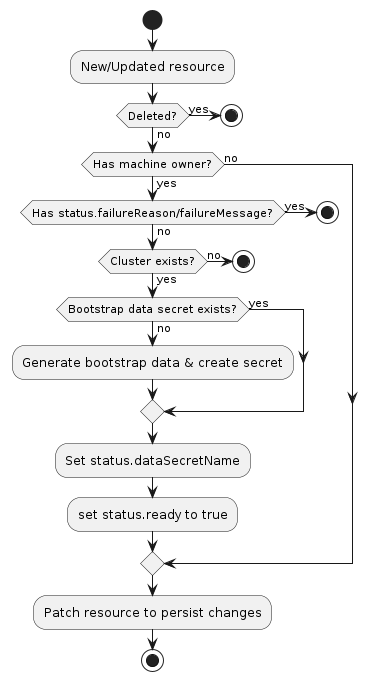
- If the resource does not have a
Machineowner, exit the reconciliation- The Cluster API
Machinereconciler populates this based on the value in theMachine‘sspec.bootstrap.configReffield.
- The Cluster API
- If the resource has
status.failureReasonorstatus.failureMessageset, exit the reconciliation - If the
Clusterto which this resource belongs cannot be found, exit the reconciliation - Deterministically generate the name for the bootstrap data secret
- Try to retrieve the
Secretwith the name from the previous step- If it does not exist, generate bootstrap data and create the
Secret
- If it does not exist, generate bootstrap data and create the
- Set
status.dataSecretNameto the generated name - Set
status.readyto true - Patch the resource to persist changes
Sentinel File
A bootstrap provider’s bootstrap data must create /run/cluster-api/bootstrap-success.complete (or C:\run\cluster-api\bootstrap-success.complete for Windows machines) upon successful bootstrapping of a Kubernetes node. This allows infrastructure providers to detect and act on bootstrap failures.
Taint Nodes at creation
A bootstrap provider can optionally taint worker nodes at creation with node.cluster.x-k8s.io/uninitialized:NoSchedule.
This taint is used to prevent workloads to be scheduled on Nodes before the node is initialized by Cluster API.
As of today the Node initialization consists of syncing labels from Machines to Nodes. Once the labels have been
initially synced the taint is removed form the Node.
RBAC
Provider controller
A bootstrap provider must have RBAC permissions for the types it defines, as well as the bootstrap data Secret
resources it manages. If you are using kubebuilder to generate new API types, these permissions should be configured
for you automatically. For example, the Kubeadm bootstrap provider the following configuration for its KubeadmConfig
type:
// +kubebuilder:rbac:groups=bootstrap.cluster.x-k8s.io,resources=kubeadmconfigs;kubeadmconfigs/status,verbs=get;list;watch;create;update;patch;delete
// +kubebuilder:rbac:groups="",resources=secrets,verbs=get;list;watch;create;update;patch;delete
A bootstrap provider may also need RBAC permissions for other types, such as Cluster. If you need
read-only access, you can limit the permissions to get, list, and watch. The following
configuration can be used for retrieving Cluster resources:
// +kubebuilder:rbac:groups=cluster.x-k8s.io,resources=clusters;clusters/status,verbs=get;list;watch
Cluster API controllers
The Cluster API controller for Machine resources is configured with full read/write RBAC permissions for all resources
in the bootstrap.cluster.x-k8s.io API group. This group represents all bootstrap providers for SIG Cluster
Lifecycle-sponsored provider subprojects. If you are writing a provider not sponsored by the SIG, you must add new RBAC
permissions for the Cluster API manager-role role, granting it full read/write access to the bootstrap resource in
your API group.
Note, the write permissions allow the Machine controller to set owner references and labels on the bootstrap
resources; they are not used for general mutations of these resources.